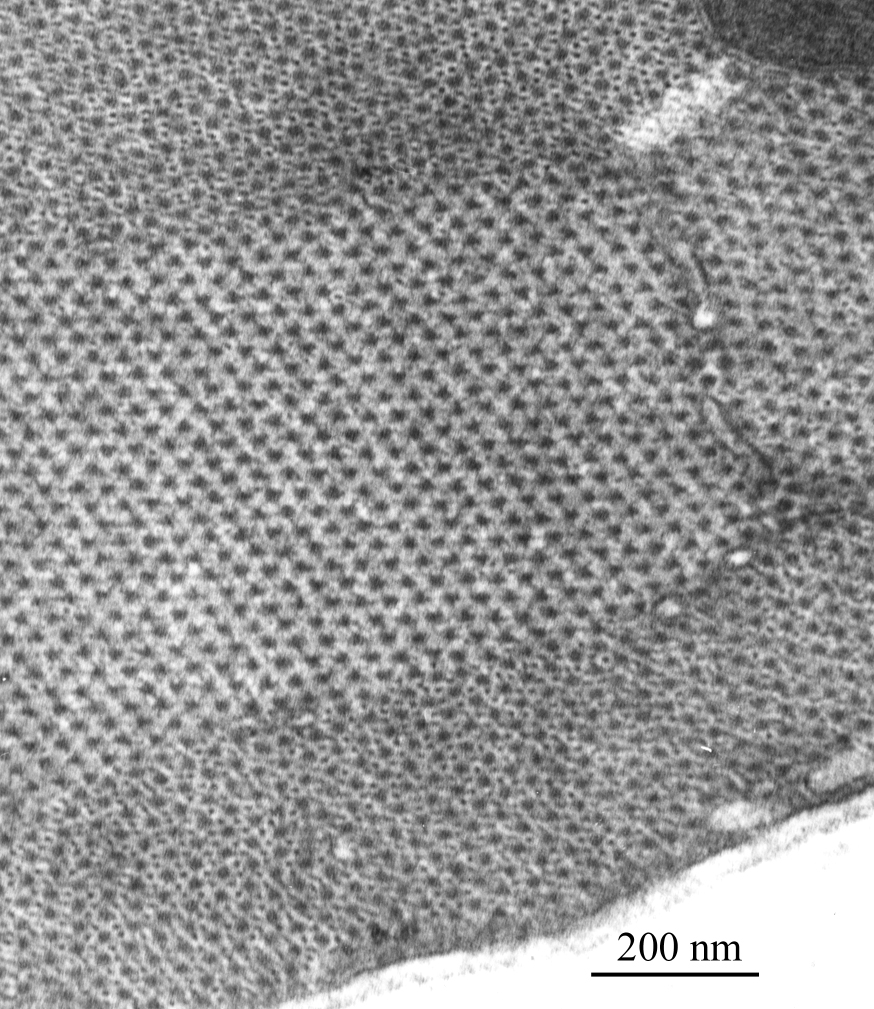
Image above: Electron micrograph image showing part of a skeletal muscle fibre, sectioned transversely across the length of the fibre, courtesy of Dr R W Banks.
Skeletal Muscle Fibre
An electron micrograph showing part of a skeletal muscle fibre, sectioned transversely across the length of the fibre. The larger dots in hexagonal array are cross-sections of thick filaments formed mostly of the protein myosin. In the upper and lower parts of the image additional, smaller, dots may be seen. These are cross-sections of thin filaments formed mostly of the protein actin. Notice that each thick filament is surrounded by six thin filaments. Sliding together of the thick and thin filaments is the basis of muscle contraction. The section was cut at about 80 nanometres thickness, with a glass knife, from chemically fixed and dehydrated tissue embedded in epoxy resin. Lead citrate and uranyl acetate “stains” were used to provide contrast in the electron microscope.


/prod01/prodbucket01/media/durham-university/research-/new-research-and-business/Research-and-Business-Partnerships.png)